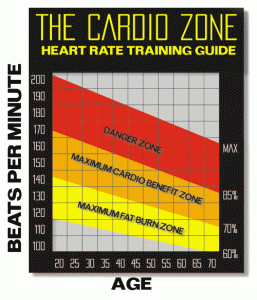
One of the questions clients often ask me is whether they should be working in the ‘fat-burning’ zone in order to lose weight when using cardiovascular equipment such as exercise bikes, elliptical trainers and treadmills.
The so-called ‘fat burning’ zone is typically defined as a moderate intensity, of between 55 and 70% of an individual’s maximum heart rate (note: to calculate your maximum heart rate, subtract your age from 220 beats per minute) you can use a heart rate monitor such as the polar ft4 to find your heart rate
Fact No. 1
The fat-burning zone is a myth based loosely on human physiology, and grossly misinterpreted.
Fact No. 2
When you exercise you burn more calories that you do if you were sitting still – no brainer!
The energy to fuel this exercise comes from two main sources – sugars and fats.
Sugar is stored as glycogen in your muscles and livers, and fats come from free fatty acids stored in your blood and fat cells.
During exercise, you will use both sources to provide energy for the exercise session – the relative proportions depend on the duration and intensity of the exercise and individual variation.
However, none of this really matters as this is just telling you where the energy to fuel the exercise session comes from – and not what happens during the other 23+hours of the day!
Fact No. 3
Losing weight from exercise alone is difficult, and weight loss works best if exercise is combined with appropriate changes to the diet.
In order to maximise weight loss from exercise, the key is to burn as many calories as possible! You can do this by working at a moderate (a.k.a. ‘fat-burning) intensity for long periods of time – but let’s be honest, who really wants to spend hours exercising?
Fact No. 4
You will burn more calories during the exercise session if you work at a more intense level (assuming the duration is the same).
Fact No.5
You will burn more calories after the exercise session if you work at a more intense level. This is called post-exercise thermogenesis and accounts for calorie burn due to a raised metabolism for a period of hours after completing an exercise session.
Doing very high-intensity intervals of between 30 seconds and 3 minutes, followed by rest periods at an easier intensity will result in even bigger boosts to your metabolism following a training session!
Fact No. 6
Not only will you burn more calories during and after an exercise session by working at a more intense level, but you will get fitter!
The recommended training zone for healthy individuals who wish to improve their cardiovascular fitness levels is between 70 and 85% of their maximum heart rate.
This article was written by Sheona Bird, nutritionist and fitness specialist.
 Optimum Fitness Fitness News and equipment reviews
Optimum Fitness Fitness News and equipment reviews